...
FindJunctions is a Java program that uses spliced alignments to identify and quantify exon-exon junctions in RNA-Seq data. When given a BAM file, it produces a BED file that summarizes every spliced aligned alignment identified in the BAM file. If also given a reference genomic sequence file (in .2bit format) it attempts to identify the strand of origin for each junction by looking for canonical intron splice junction sequences.
You can also run FindJunctions within Integrated Genome Browser.
How to use FindJunctions
...
You can view FindJunctions by:
...
within IGB
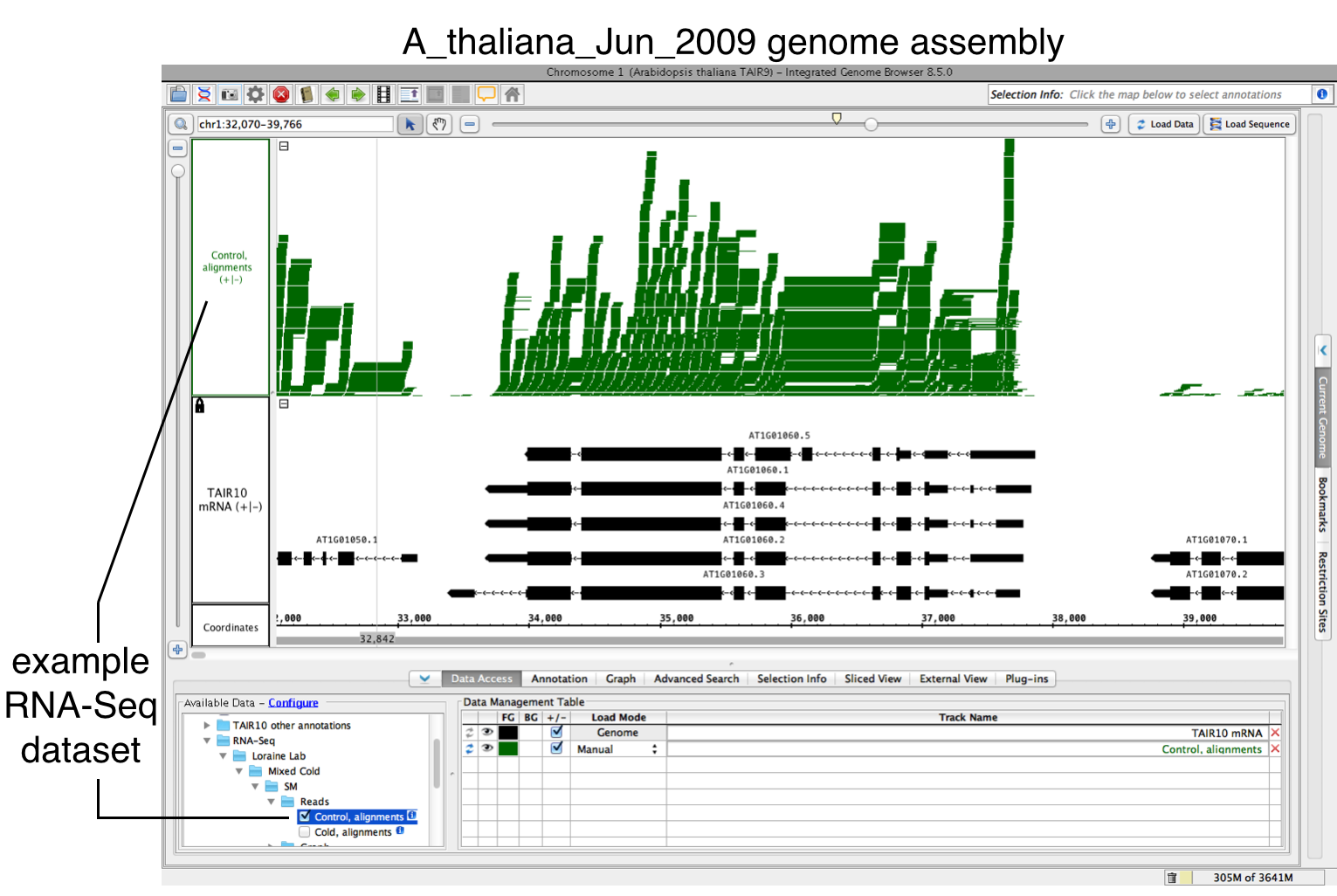
To use FindJunctions within IGB, first load a BAM file:.
- Open BAM file.
- Zoom in on the gene or region of interest.
- Click on Load Data.
Run FindJunctions:
...
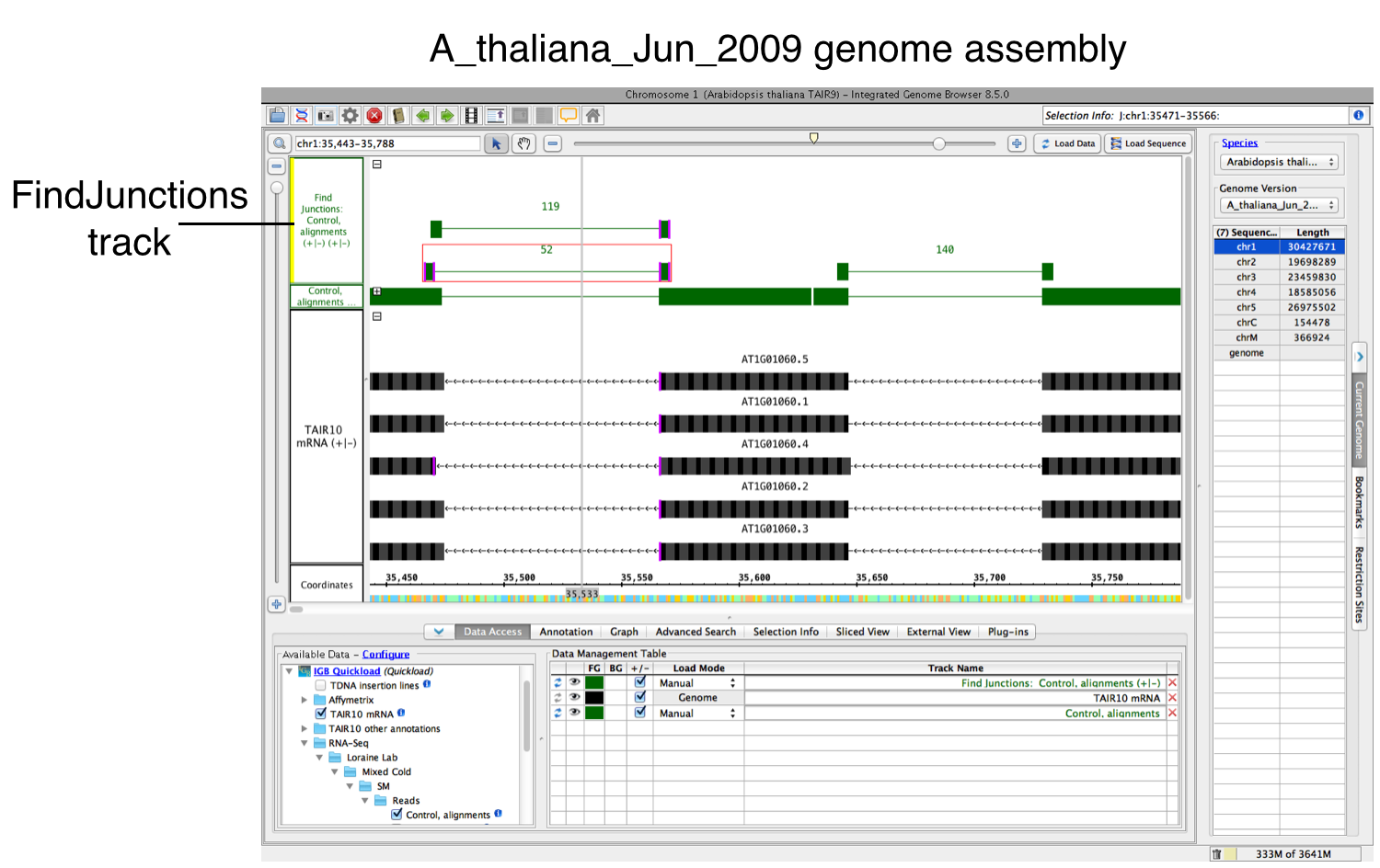
- Right-click on the track, and select Track Operations > FindJunctions.
- Click on OK.
FindJunctions will appear as a new track. Brackets represent splice junctions across exons. The number of reads supporting each splice junction is shown above each bracket.
The default behavior for FindJunctions is to identify split reads with a minimum of five base pairs on either side of the exon.
You can change the default FindJunctions behavior by:
- Right-clicking on the track, and selecting Track Operations > FindJunctions.
- Inputting a new number in the threshold box (default is 5).
How to get FindJunctions without IGB
- RNA-Seq track label
- Select Track Operations > FindJunctions
- Enter a value or use the default. At least this many bases must align across a putative intron for a read to be counted as support for a junction.
- Select OK to run FindJunctions.
A new track will then appear containing junction features bracketing introns. Labels report the number of spliced alignments that supported the junction.
...
Using FindJunctions from the command line
To run FindJunctions as a stand-alone program, visit https://bitbucket.org/lorainelab/findjunctions
Using the jar file to run FindJunction
To run the program from the command line, you would do something like:
| Code Block |
|---|
java -Xmx1g -jar FindJunction_exe.jar -u -n 5 -b Genome.2bit -o FJ.bed sample1.bam,sample2.bam
|
In this example, the -Xmx1g option specifies that the program can run with up to 1 Gb of computer memory (RAM) using the code in jar file (-jar) FindJunction_exe.jar. The Follow the instructions to compile FindJunctions and create a "jar" file.
Then run the program using java, providing a comma-separated list of BAM files.
Options:
- -u option (for unique)
...
- ensures that only uniquely mapping spliced reads (with NH tag equal to 1) will be used to construct junctions.
...
- -n option is the number of bases that must map to either side of a putative intron for a spliced read to be used to create or support a junction feature.
...
- -b
...
- is the absolute full path to the .2bit genomic sequence file that will be used to identify junction strand
...
- -o (output)
...
- is the name of the junctions
...
- file that will be written.
...
Output is tab-delimited BED12 format. The name field contains a name constructed from the location of the junction and the score field contains the number of spliced alignments used to create the junction feature.supporting each junction.
Example)
| Code Block |
|---|
java -Xmx1g -jar FindJunction_exe.jar -u -n 5 -b Genome.2bit -o FJ.bed sample1.bam,sample2.bam
|
Here, -Xmx1g option specifies that the program can run with up to 1 Gb of computer memory (RAM) using the code in jar file (-jar) FindJunction_exe.jar.