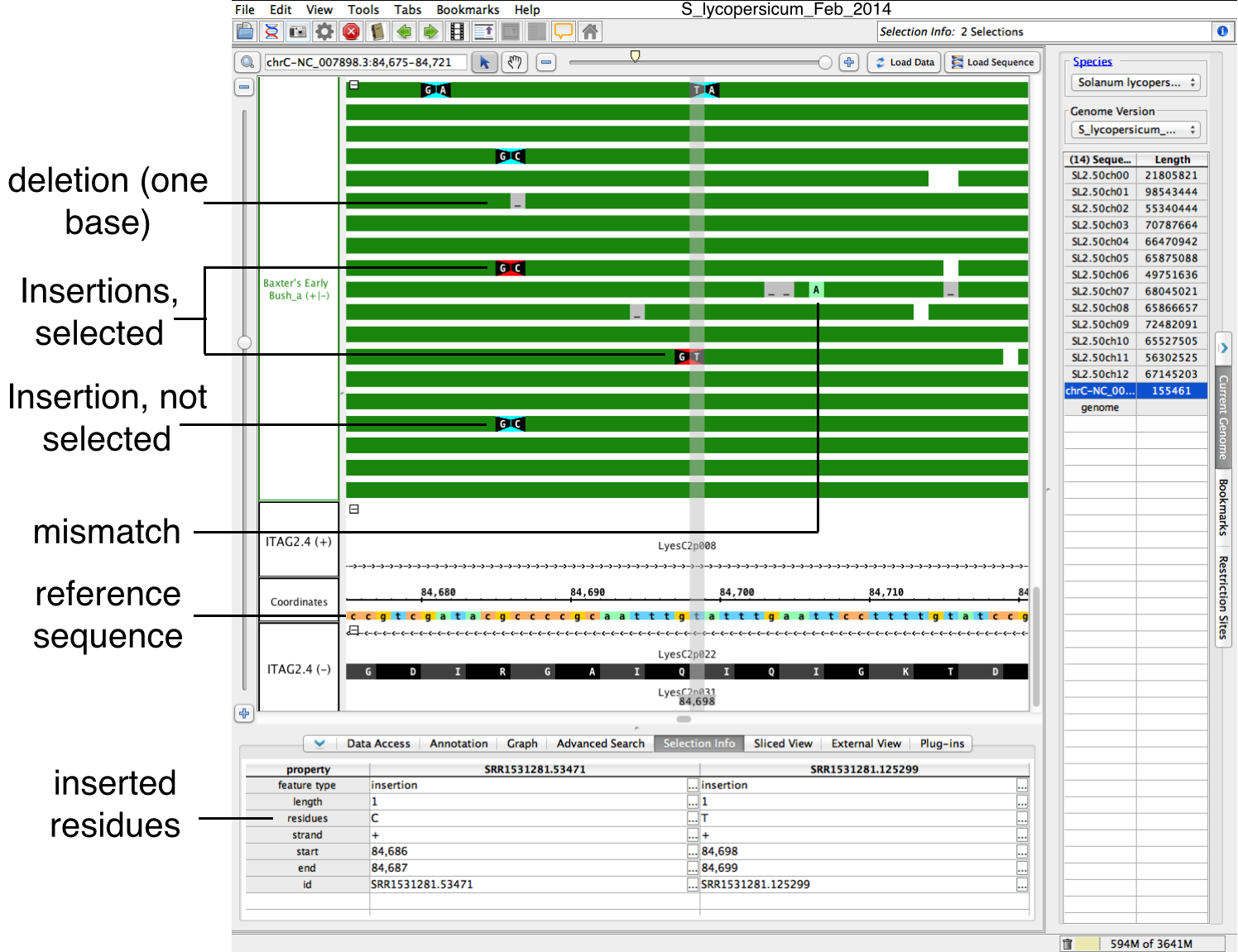
IGB displays insertions, deletions and mismatches as color-coded bases and icons on top of read alignments, as shown in the following image.follows:
Insertions -
basesResidues flanking insertion site
appearare shown in
whiteblack with a
black backgroundwhite background by default (purple on white here); triangular shapes between them point
atto the location of the inserted base
or bases that are(s) present in the aligned sequence but not in the reference.
Select an insertion and the Selection Info tab to display the sequence of inserted bases
- Deletions - bases Residues deleted in the aligned sequenced relative to the reference appear in gray with underscore charactersthe reference appear as horizontal lines that are of the same color and connect flanking residues.
- Mismatches - bases Residues in the aligned sequence that do not match the corresponding base in the reference appear as higlighted highlighted bases. To highlight mismatches, click Load Sequence
Use the zoom stripe (shown in gray) as a guide to compare mismatches, deletions, and insertions between different read alignments and the reference.
...
Insertions, Deletions, and Mismatches in IGB
To re-create this scene in IGB:
- Open tomato genome S_lycopersicum_Feb_2014 (ITAG2.4)
- Select Current Genome > chrC-NC_007898.3 (tomato chloroplast genome)
- Click Load Sequence to load chloroplast genome sequence
- Zoom to chrC-NC_007898.3:72,724-102,016 (enter in Quick Search box, top left)
- Select Data Access > Available Data > Plastid Resquencing > Baxter's Early Bush_a
- Click Load Data to load alignments for Baxter's Early Bush tomato cultivar
- Expand stack height to 150 reads per track (right-click track and select Set Stack Height)
- Use vertical zoomer to stretch read alignments vertically
- Enter chrC-NC_007898.3:84,675-84,721 in Quick Search box to zoom to region
- Scroll down until the reference sequence comes into view