| Table of Contents |
|---|
Introduction
Graphs contain Genome graphs consist numerical data associated with base pair positions along the chromosome sequence axis, such as sets of scores or chromosome copy numbers at specific positions. IGB allows you to visualize such graph data and compare it with RefSeq and other annotations.
Examples of suitable data include:
...
. You can open and view genome graph data files in IGB. Using the Graph tab, you can display graphs as line graphs or heat graphs, change the minimum and maximum values shown on a graph, or perform calculations on graphs.
You can also create graphs from annotation tracks, such as an RNA-Seq coverage graph showing the number of read alignments starting at each position.
Other examples of genome graphs include:
- Expression values from genome tiling arrays.
- Density of ESTs across Percentage methylation across chromosomes
- GC content along chromosomes
- Measures of conservation between two genomes
There are two basic types of genomes graphs:
- Position graphs associate scores with single genomic positions.
- Interval graphs associate scores with ranges of genomic positions.
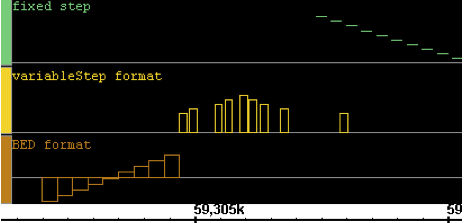
Here is a very simple are simples example of several three interval graphs:
Loading graph files
Graph files are loaded in the same way as annotation data files. To open graph files, see instructions for Loading data.
IGB can display graphs in several file formats, developed at Affymetrix or elsewhere. All file names must include the file name extension, such as '.sgr'. Compressed files must include the graph type extension AND the compression extension, such as "mygraph.sgr.zip". For the list of all file formats IGB supports, see File Formats.Graph files in some formats (notably .gr) do not contain information about which genomes and chromosomes they correspond to, so be sure to set Species and Genome Version before or as part of loading these files. These may be loaded and displayed alongside annotations on any chromosome, but the data may have no meaning if compared to the a chromosome it was not designed for. i.e., to use a .gr file, you must first load the proper organism, genome AND chromosome prior to loading the .gr file
Hiding and deleting graphs
...