| Table of Contents |
|---|
Introduction
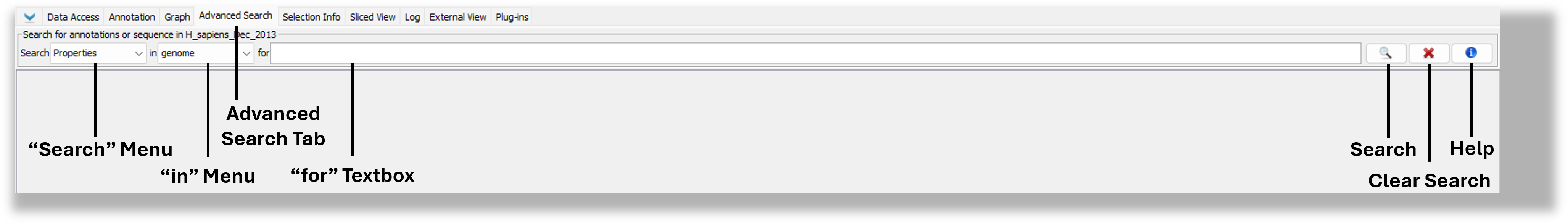
Use the Advanced Search tab to search for gene annotations or sequence residues or annotations. Both search types support regular expressions and wild card characters (see the "Regular expression, wild cards, and nucleotide symbols" section below).
Using advanced search Advanced Search, you can:
- look Look up genes or other annotations by keyword, name , or idkeyword
- find for Find instances of a transcription factor binding sites
- display Display locations of PCR primers
Search results will appear in the Advanced Search tab in a results table. Double-click a row in the table to view the result in the main IGB window.
If you search for sequence residues, IGB will also display color-coded bars in the coordinates track indicating the matched sequence.
Search types
The Advanced Search supports:
- ID, Name, or nameTitle - find features annotations by name
- Keyword - find features annotations by keyword
- Residues find patterns in genomic sequence - find sequences or regular expressions
Search by ID, Name, or Title
ID, Name
...
, or Title search will search IDs and names of annotations.
To find a feature or an annotation by ID, Name, or nameTitle:
- Select IDs or names ID, Name, or Title from the Search menu.
- Choose "genome" or a specific chromosome to search from the in menu.
- Enter the ID or gene name of the annotation you want to find (for textbox).
- Press <Enter> key or click the Search button.
Only data already loaded into the IGB viewer will be searched.IDs or Names search will search IDs and names of annotations.
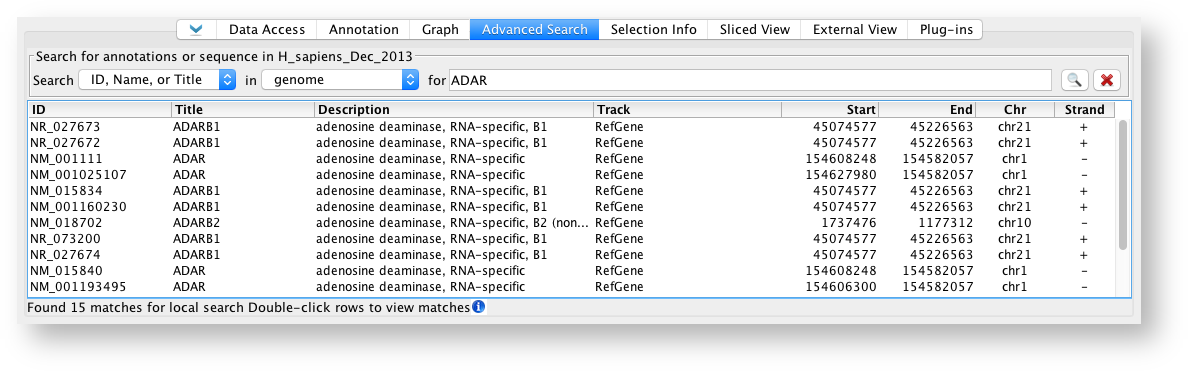
ID, Name, or Title Search Results
Search by Keyword
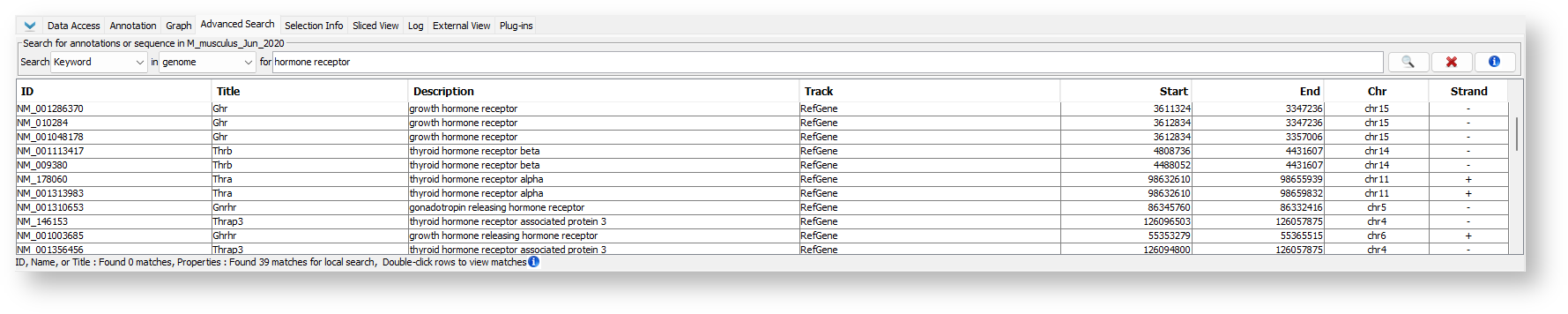
Keyword search, similar to ID, Name, or name Title search, will search annotation namesIDs, but it will also search other information associated with annotations , such as descriptions or and other attributes. Choose Keyword to search descriptions, names, ids, and other attributes.
Results will appear in the Search Results table. Double-click a row in the table to zoom to that feature.
Advanced Search tabbed panel after searching the human genome
...
To find an annotation by Keyword:
- Select Keyword from the Search menu.
- Choose "genome" or a specific chromosome from the in menu.
- Enter the keyword you want to search for (for textbox).
- Press <Enter> key or click the Search button.
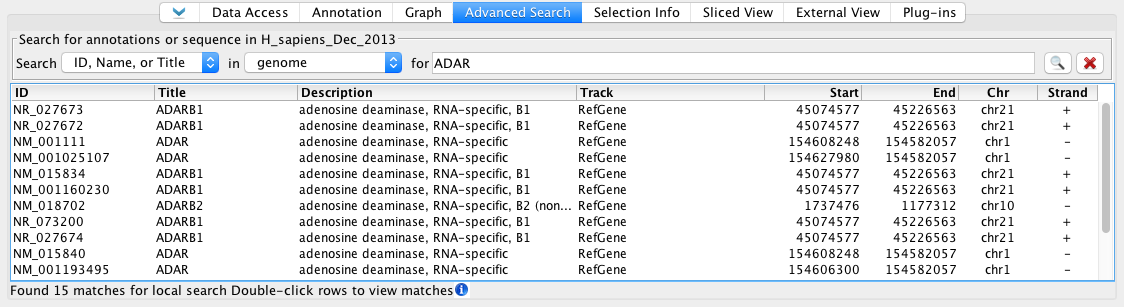
Keyword Search Results
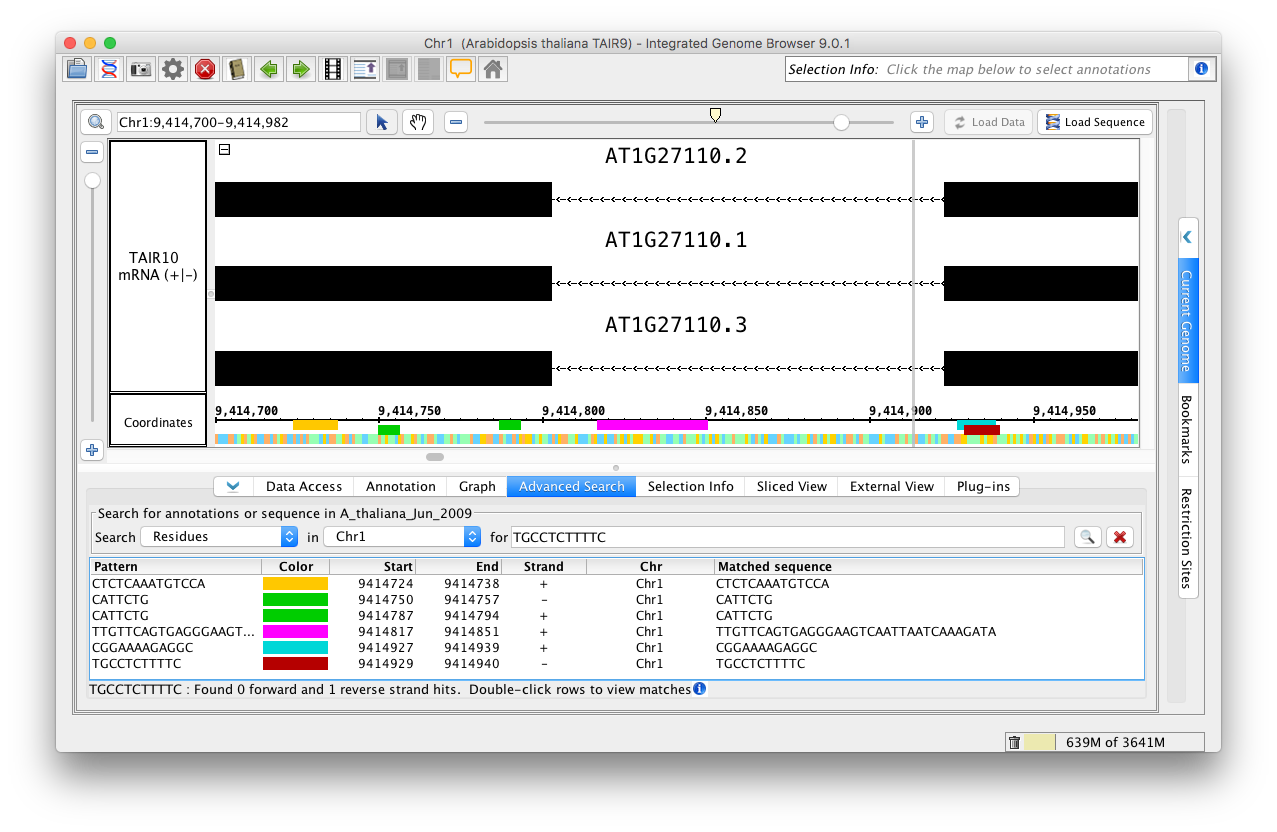
Search by Residues
To find all instances of a sequence or regular expression:
- Select Residues from the Search menu
- Choose chromosome to search from "genome" or a specific chromosome from the in menu.
- Enter the sequence or regular expression you want to find (for textbox).
- Press <Enter> key or click the Search button.
- Enter new search terms. Notice that IGB will overlay results, preserving results from previous searches.
IGB displays matches in the results table and as colored bars underneath the coordinates axis. Matches on the minus strand appear in a slightly lower position.
Residue search results.
Searching for multiple residues simultaneously
To search for multiple residues simultaneously enter residues in advanced search box separated with the pipe (|) symbol.
Example: atgttc|atggc
This will return a search for atgttc and atggc separately.
Residues Search Results
Regular expression, wild cards, and nucleotide symbols
...
Searching by nucleotide symbols is available in IGB versions 9.1.12 and above.
Example queries:
Pattern | Represents | Example | Finds |
. |
Any single nucleotide | ACCT.T | ACCTTT, ACCTAT, ACCTGT, and ACCTCT (4 possibilities) |
.. |
Any two nucleotides | ACCT..T | ACCTAAT, ACCTATT, ACTAGT, Etc. (4 x 4 possibilities) | |
[CG] | C or G | ACCT[CG]TC | ACCTCTC and ACCTGTC |
| X|Y | X or Y | ATC|AAG | ATC and AAG |
T{1,n} | 1 to n T's | ACGGT{1,3}C | ACGGTC, ACGGTTC, ACGGTTTC |
T* | Zero or more T's | ACGGT*C | ACGGC, ACGGTC, ACGGTTC, ACGGTTTC, ACGGTTTTTTTTTTTTTTTTTTTTTTTTTTTC, Etc. |
.*? |
A string of any length containing any nucleotides | TCGGGGTTAA.*?CTGGACTC | Many possibilities. Because this allows for so many possibilities, it only recommended with a limited scope of search and/or with very specific (several specified base pairs) on both ends. |
.* |
The longest possible string of any length containing any nucleotides | TCGGGGTTAA.*CTGGACTC | Differs from the search above in that the longest possible result(s) will be found. Bear in mind that the result returned from this search with depend on the scope of the search, |
i.e., how much of the genomic sequence has been loaded and is available for searching. | |||
| R | A or G | GCCR | GCCA, GCCG |
| Y | C or T | AGCY | AGCC, AGCT |
| S | G or C | AGCS | AGCG, AGCC |
| W | A or T | AGCW | AGCA, AGCT |
| K | G or T | AGCK | AGCG, AGCT |
| M | A or C | AGCM | AGCA, AGCC |
| B | C or G or T | AGCB | AGCC, AGCG, AGCT |
| D | A or G or T | AGCD | AGCA, AGCG, AGCT |
| H | A or C or T | AGCH | AGCA, AGCC, AGCT |
| V | A or C or G | AGCV | AGCA, AGCC, AGCG |
| N |
| Any base (i.e., A or G or T or C) | AGCN | AGCA, AGCG, AGCT, AGCC | |
| \QN\E | N | AGC\QNNN\E | AGCNNN |
More information about regular expressions is available from http://docs.oracle.com/javase/7/docs/index.html this Java Regex Cheat Sheet.